Unit 5: Crisis and Change
Lesson H: From Hot to Cold War
Lesson Overview
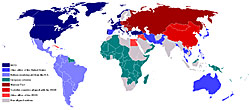
Tensions between the United States and the U.S.S.R. escalated quickly after World War II and led to a Cold War. The Cold War was not an isolated event or a conflict simply between the United States and the U.S.S.R.; the Cold War enveloped many countries around the world. These Cold War contenders wanted to spread their respective economic ideologies and political structures as well, and, thereby spread their spheres of influence. This led to regional conflicts as part of the larger Cold War.
Key Questions
- What are the causes, events, and consequences of the Chinese Revolution?
- How does the Chinese communist system compare with that in the U.S.S.R.?
- What is the role that the Chinese played in the wars in Korea, Cuba, Vietnam, and Cambodia?
- How did regional wars, conflicts, and nationalistic movements become part of the larger Cold War?
Student Outcomes
- Analyze the causes, events, and consequences of the Chinese Revolution, including the roles of Chiang Kai-shek (Jiang Jieshi), Mao Zedong, and the creation of Taiwan.
- Compare the Chinese communist system with that in the U.S.S.R.
- Analyze the factors that led to the Cold War, including atomic weapons, Soviet expansion in Eastern Europe, and the ideological differences between democracy, totalitarianism, capitalism, and communism.
- Explain the concepts of "West" and "East" during the Cold War.
- Describe the reactions of the U.S.S.R. to the United Nations, the Truman Doctrine, the Marshall Plan, and NATO.
- Compare the reactions of different peoples to events of the Cold War, such as European resistance in Hungary and Prague Spring and the reactions in non-aligned nations.
- Obtain historical data from a variety of sources. (Historical Thinking Skill)
Key Terms
- Berlin Blockade
- capitalism
- Cold War
- communism
- détente
- dictator
- domino theory
- Eastern Bloc
- Iron Curtain
- Marshall Plan
- nationalism
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Prague Spring
- proxy war
- revolution
- satellite countries
- trade embargo
- Truman Doctrine
- Warsaw Pact
Student Resources
- Influence in the Two-Sided Cold War (doc)
- Chinese Communist Revolution Graphic Organizer (doc)
- The Cold War Expands Jigsaw Graphic Organizer (doc)
- Regional Conflict in the Cold War Brief Constructed Response (BCR) (doc)
Chart of Activities:
| Activities to Complete | Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Pre-Assessment | 10 minutes |
| Activator: Changes in the Postwar World, 1945-1975 | 15 minutes |
| Opening: A Bipolar World | 10 minutes |
| Activity 1: Marshall Plan and Truman Doctrine | 15 minutes |
| Activity 2: East vs West - NATO and the Warsaw Pact | 20 minutes |
| Activity 3: Influence in the Two-Sided Cold War | 20 minutes |
| Activity 4: The Chinese Communist Revolution | 20 minutes |
| Activity 5: China and the U.S.S.R. | 20 minutes |
| Activity 6: The Cold War Expands | 60 minutes |
| Review and Assessment | 30 minutes |
| Lesson Summary | 5 minutes |
Lesson Completion Time
The total estimated time to complete this lesson is 225 minutes.
Page Notes:
[1] Source: This image from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Cold_War_Map_1959.png is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 3.0 License. Attribution: Hoshie.